

We highlight existing data to support the use of oxantel pamoate against T. trichiura than the currently recommended drugs, which makes it a strong asset to the depleted drug armamentarium and could help delay or even prevent the development of resistance to existing drugs. trichiura and suggest that oxantel pamoate is more efficacious against T. Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of this drug against T. Oxantel pamoate was found to be safe in humans, with only a few mild adverse events reported. The drug is metabolically stable, shows low permeability and low systemic bioavailability after oral use. Oxantel pamoate acts locally in the human gastrointestinal tract and binds to the parasite’s nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), leading to a spastic paralysis of the worm and subsequent expulsion. This review summarizes the current knowledge on oxantel pamoate and its use against T. trichiura infections (estimated 76% cure rate and 85% egg reduction rate at a 20 mg/kg dose). Oxantel, a tetrahydropyrimidine derivative discovered in the 1970s, has recently been brought back to our attention given its high efficacy against T. However, they are only moderately efficacious against hookworm and poorly efficacious against T. The currently available drugs are all highly efficacious against A.

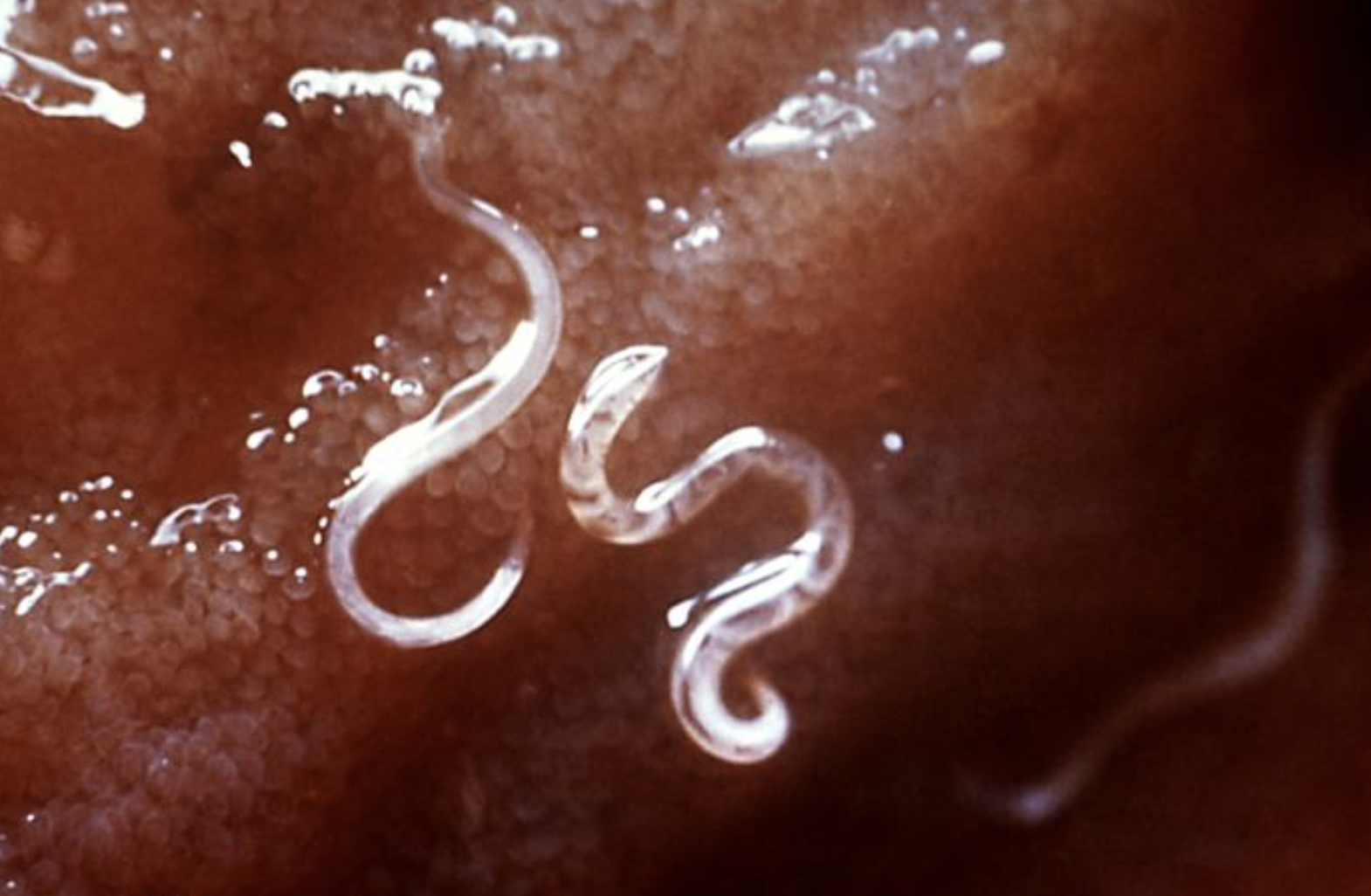
Soil-transmitted helminths ( Ascaris lumbricoides, hookworm and Trichuris trichiura) infect about one-fifth of the world’s population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
